More than 55% of the world’s population is living in urban areas today. Cities are facing increasing problems caused by rapid urbanization, which cannot be supported by an aging city infrastructure. The percentage of the global population living in cities is projected to rise to 66% by 2050. As a result there are growing concerns regarding clean water, waste management, transportation infrastructure, adequate healthcare, access to education, as well as safety for urban residents, to name just a few. There is consensus among thought leaders that we need a new approach that allows us to move towards Smart Sustainable Scalable Communities (S3C).

Smart
“A smart city uses Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) to enhance the quality and performance of urban services, to reduce costs and resource consumption, and to engage more effectively with its citizens.” (source)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the most disruptive evolution of ICT. One of its most significant impacts is on urban development. It provides radically new ways to implement resource efficient, sustainable, and scalable city operations.
Sustainable
“A sustainable, resource efficient city can be defined as a city that is significantly decoupled from resource exploitation and ecological impacts and is socioeconomically and ecologically sustainable in the long term.” (source)
Sustainable communities are inclusive, reflecting the character and needs of the population, including for social inclusion and economic empowerment. They also are resource efficient, reducing their environmental footprint.
Scalable
“The major shifts toward cities has created critical challenges. In the Global South and East, the scale and pace of urbanization is straining physical infrastructure, fiscal capacity and natural resources in many places. It is challenging institutional and political structures that often lack the capacity and flexibility to respond.” (source)
The second wave of urbanization, already underway, equates to tremendous and rapid growth of cities. Any community being developed must plan for this, and incorporate scalability in the design of its physical and virtual infrastructure, economic underpinnings, and social basis. Planning and investment need to account for growth from the outset.
Communities
“Self-organized network of people with a common agenda, cause of interest who collaborate by sharing ideas, information and other resources.” (source)
Communities will form the basis for new cities as well as for segments of a city that may evolve to be more sustainable. Engaging communities in designing their future cities will more effectively achieve the necessary shift in lifestyle to higher resource efficiency and structured social engagement.
The ideal S3C is based on a holistic integration of the natural environment, city infrastructure, ICT hardware and software. ICT is a critical component of a city's transformation into a S3C. Smart, connected technologies can provide crucial information for city managers such that they can increase the efficiency of urban services, it can improve the quality of life of citizens, be a catalyst for economic growth, increase the resilience against natural disasters and provide for better management in case they happen, and improve the city's sustainability.
CSRspace utilizes two essential tools to guide a developing community towards the goal of becoming a S3C: the S3C Framework and the Living Lab.
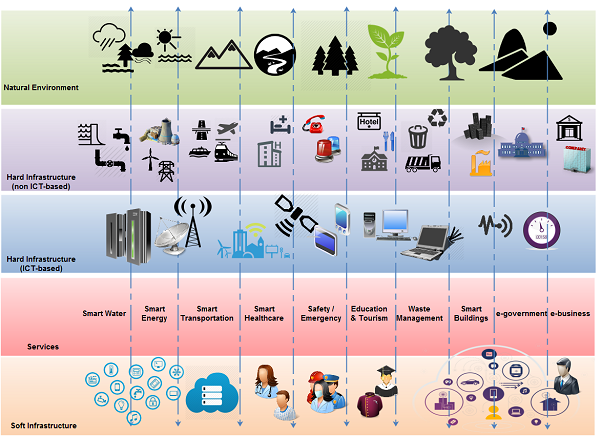
S3C Framework
The S3C Framework is a tool that illustrates the capabilities of smart city technologies such that stakeholders understand what is possible and can express their requirements beyond their traditional thinking; on the other hand it helps planners to map desired outcomes onto the typical structure of a S3C, which accelerates the progress towards a S3C design.
Living Lab
Many Smart Cities today employ the concept of a Living Lab: new technologies as well as new approaches to city management are tested in a real-life city environment, allowing users to give feedback and providers to adapt their solutions. The goal is to implement an open collaborative approach to innovation that includes all stakeholders.
