Understanding the Internet of Things (IoT)
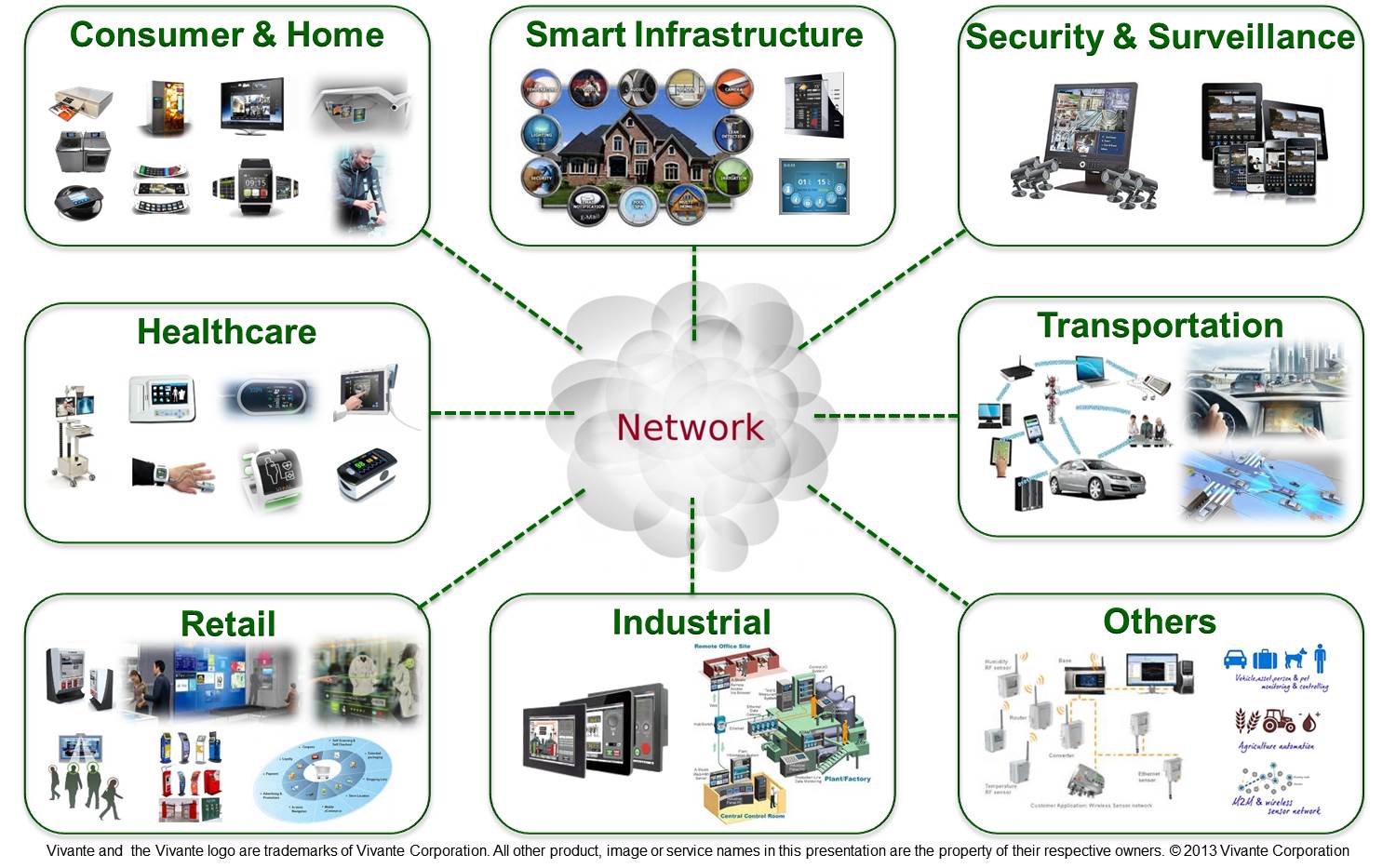
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the most disruptive technology. It will impact every industry in every economy around the globe. Analysts frame it as the third revolution, succeeding the industrial and Internet revolution, but with a Total Value at Stake that is much larger – in the order of $15 Trillion, a quarter of global GDP.
An estimated 50 Billion physical objects will be connected to the Internet by 2020, including home automation, manufacturing plants, health care systems, mining and oil industries, energy grids, and precision farming, to name just a few. One of the key areas that will be impacted are cities. The rise of the Smart City is based on sensor networks that monitor and manage all city infrastructure.
CSRspace provides IoT Education to help clients understand the various components of IoT solutions.
Improving urban communities through the application of Smart City technologies
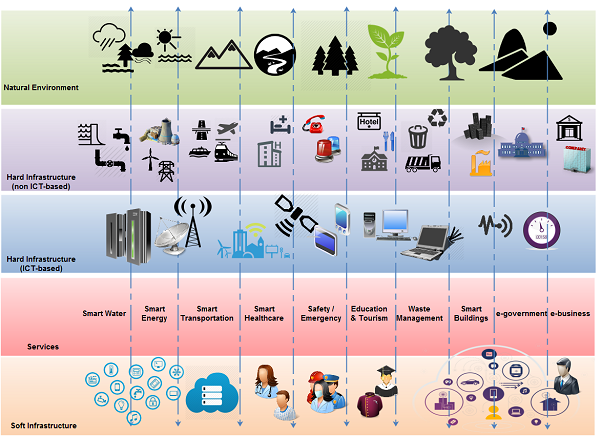
The efficiencies of a Smart City are based on the synergistic effects of managing all city infrastructure (streets, lighting, water, waste, energy, buildings, etc.) via smart connected technologies that are part of the Internet of Things (IoT).
However, this is a challenging endeavor. Most of the technologies are new and city planners are often not familiar with the possibilities and limitations. Furthermore, while efficiencies can be gained by point solutions (e.g. a smart irrigation system to reduce water usage), the real benefits of a truly Smart City can only be achieved by applying systems thinking: the various infrastructures, city departments, applications, and data silos need a common foundation in order to enable holistic city management.
CSRspace provides Smart City education to help clients understand how to effectively apply IoT technologies so that they can progress towards Smart Sustainable Scalable Communities (S3C).
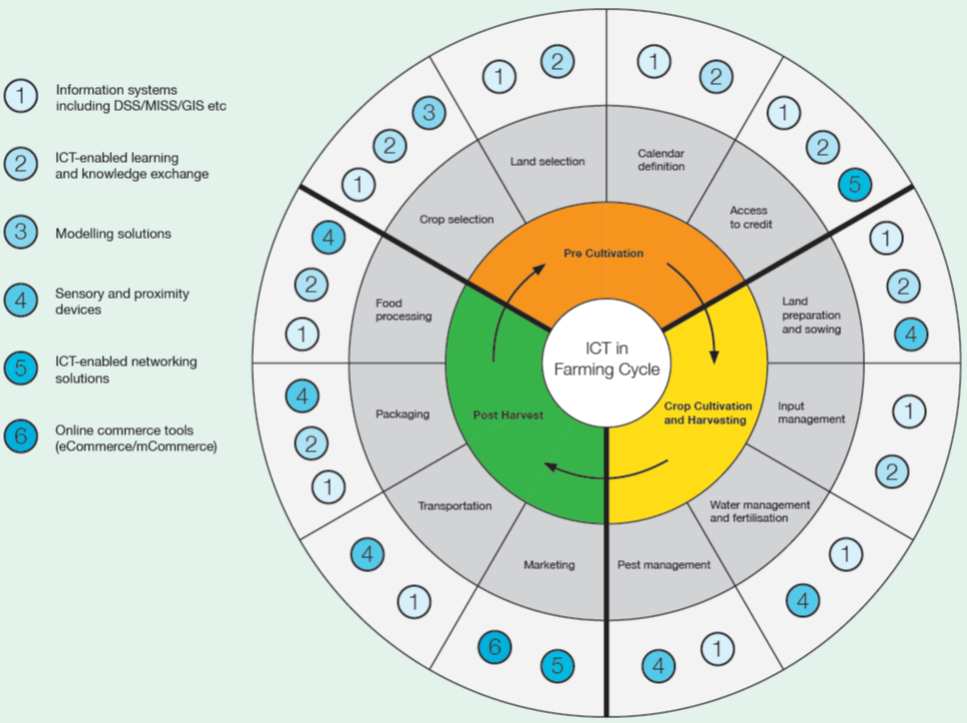
Applying smart agriculture extensions to increase competitiveness and farmer income
ICT in farming can play a major role across all phases f the farming life-cycle, including access to credit, land selection, crop selection, land preparation and sowing, irrigation and fertilization, pest management, as well as post-harvesting processes like transportation, food processing, market selection and sales optimization.
Examples of key topics include:
- Precision agriculture
- Common platforms for agriculture stakeholders
- The role of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) in agriculture
- eAgriculture knowledge sharing in Africa
- The role of mobile technology in eAgriculture
- Traceability
Enabling businesses to grow by utilizing public Cloud Service Providers
One of the major inhibitors for growth of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) on the African continent is the lack of automation of their business processes. Most SMEs cannot afford to invest in in-house IT, and there is a significant shortage of skilled labor. Public Cloud Computing offers a solution: required IT resources can be rented on a pay-as-you-go basis, whereby the elastic compute model of the public cloud allows to scale resource usage up and down following the real-time demand.
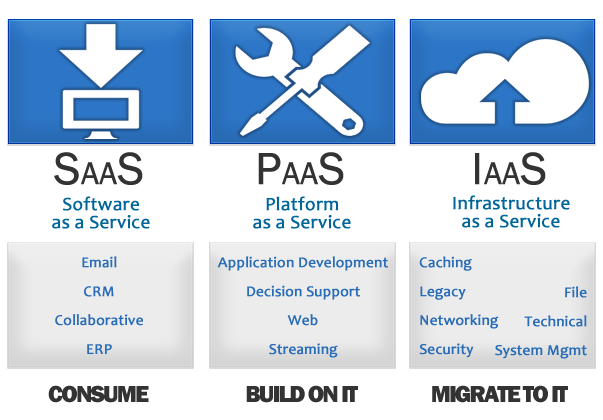
This shift from a CAPEX (Capital Expenditure) to an OPEX (Operational Expenditure) model can make IT affordable to African SMEs. The skill requirements can be minimal if Software as a Service (SaaS) applications are utilized, or significantly reduced in case of a Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) cloud since the Cloud Service Provider (CSP) manages the majority of the IT environment.
Another driving force for cloud computing is the proliferation of mobile apps that continue to become ever more popular in the African context like mobile banking and apps that cater to the specific needs of farmers.
However, the landscape of cloud computing can be confusing: different providers and technologies, deployment models (SaaS, IaaS, Platform as a Service (PaaS) and many flavors in between), security implications, and widely varying Service Level Agreements, to name a few. CSRspace helps clients to navigate the different options by developing a Cloud Computing strategy.